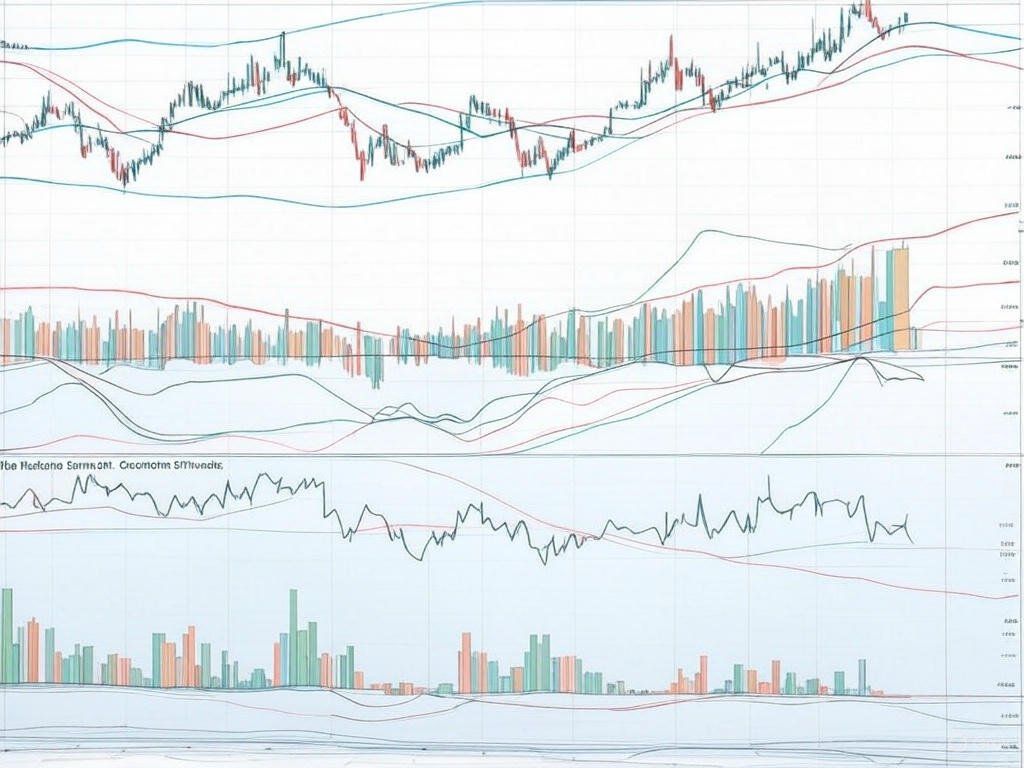
Traders and investors rely heavily on technical analysis to guide their decision-making process by analyzing price history and trading volume. Investors can anticipate price movements and align their trading strategies using stock charts and technical indicators.
Stock Charts Explained
Graphically, stock charts depict price movements through time and are visual representations of patterns that suggest future trends. The two most popular types of stock charts are:
1. Line Charts
A line chart is the simplest way to show the price movement of a stock over a period by linking the closing prices. They are great for spotting longer-term trends but do not provide much in the way of detailed trading information.
2. Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts provide the low, high, open, and close for a period of time. They provide more insight into trends and market sentiment reversals.
Technical Indicators for Trading
Stock performance is analyzed using technical indicators and traders make decisions based on this analysis. They have, Jazz Open is, a number of them for popular, including:
1. Moving Averages
“There are two main types of moving averages, the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA).” The two common types are:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): The average price for a specified period.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Puts greater emphasis on the most recent prices, making it more sensitive to shifts in prices.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI is a momentum indicator that measures the speed and change of price movements to show if a stock is overbought or oversold. A reading greater than 70 reflects overbought market conditions, while a reading less than 30 reflects oversold conditions.
3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it indicates a potential buy signal and vice versa. Designed to highlight buy and sell opportunities, it is made of two moving averages and a histogram.
4. Bollinger Bands
Senidi 1: Explanation of Bollinger Bands Bollinger Bands comprise a central moving average line with two standard deviation outer bands. Prices hitting the upper band may indicate a compulsory mallentity, and hitting the lower band may indicate over selling.
Typical Chart Patterns and What They Tell You
Based on historical price data, chart patterns assist traders in forecasting future price action. Some key patterns include:
1. Head and Shoulders
This is the indication of reversal of trend. A head and shoulders top marks a bearish reversal and an inverse head and shoulders a bullish reversal.
2. Triangles (Ascending\, Descending\, Symmetrical
Continuation patterns and reversal patterns are triangles — the direction in which they are formed determines the type of trend they indicate. An ascending triangle signals bullish breakout, while descending triangles show a bearish descent.
3. Double Top and Double Bottom Predictions
- Double Top: A bearish reversal pattern that occurs following an uptrend.
- Double Bottom: Bullish reversal pattern that forms after a downtrend.
4. Cup and Handle
A cup with a handle is a bullish continuation pattern where a stock creates a rounded bottom (the cup) followed by a small consolidation (the handle) before moving to break out upwards.
How to Make the Most of Technical Analysis
Investors can maximize the effectiveness of technical analysis by:
- Use Multiple Indicators: Following a single indicator can give false signals. Overlapping RSI, MACD and moving averages gives a solid confirmation.
- Evaluate Volume Patterns: Higher volume on price movements testifies to healthy trends.
- Define Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Limits help traders to control risk and secure profits.
- Do Not Trade from the Hear: When we follow technical indicators rather than our feelings, we better follow the discipline of trading decisions.
- Demo Accounts: Traders should practice trading using a demo account before investing actual money.
Technical AnalysisIn the Real World
Example 1: A Bullish Trend Location
A stock is trading above its 50-day moving average with an RSI under 70. This confirms an uptrend so the trader buys shares.
Example 2: Identifying a Bearish Reversal
A stock makes a head and shoulders formation, but on decreasing trading volume. Bearish crossover on MACD raises red flag The trader closes out their position to minimize losses.
Drawbacks of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a very useful tool, but it does have its limits:
- It ignores basic drivers such as company profits and economic circumstances.
- Historical Price Patterns Are Not Always Indicative Of Future Performance
- It may give a false signal and predict wrong.
Conclusion
Traders are heavily dependent on technical analysis, which helps them anticipate how stock prices will move based on information from the past and on market trends. Exploring chart patterns, timeframes, indicators, and trading strategies can aid stock investors in stock investment.